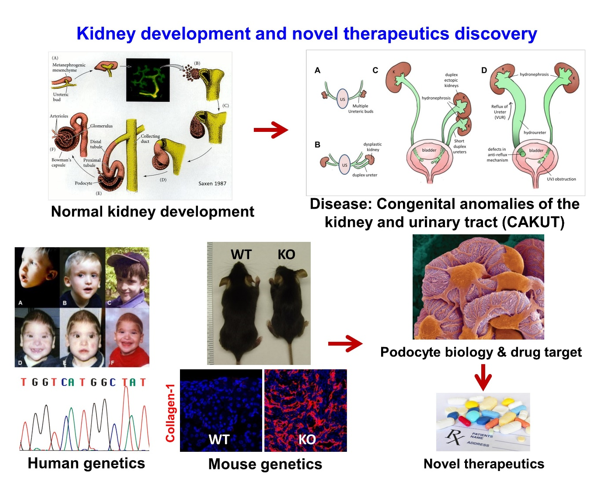
The Lu Lab focuses on basic and translational research of kidney development, congenital anomalies of the kidney and urinary tract (CAKUT), podocyte biology and injury, renal stromal cell biology and kidney fibrosis, and discovery of novel drug targets for chronic kidney disease. Lu Lab research program is supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and Pfizer’s Centers for Therapeutic Innovation (CTI).
Five selected publications:
- Lu W et al. Disruption of ROBO2 is associated with urinary tract anomalies and confers risk of vesicoureteral reflux. American Journal Human Genetics, 2007. PMID 17357069
- Fan X et al. Inhibitory effects of Robo2 on nephrin: a crosstalk between positive and negative signals regulating podocyte structure. Cell Reports, 2012. PMID: 22840396
- Rasouly HM et al. Loss of Zeb2 in mesenchyme-derived nephrons causes primary glomerulocystic kidney disease. Kidney International, 2016. PMID: 27591083
- Fan X et al. SLIT2/ROBO2 signaling pathway inhibits nonmuscle myosin IIA activity and destabilizes kidney podocyte adhesion. JCI Insight, 2016. PMID: 27882344
- Pisarek-Horowitz A et al. Loss of roundabout guidance receptor 2 (Robo2) in podocytes protects adult mice from glomerular injury by maintaining podocyte foot process structure. American Journal of Pathology, 2020. PMID: 32220420