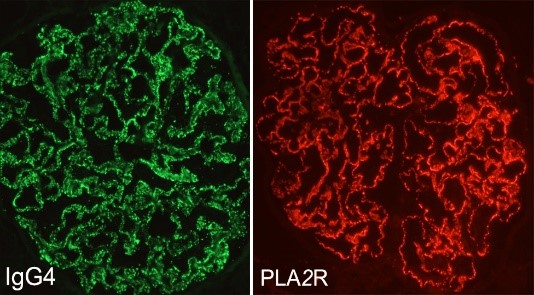
The Beck / Salant lab explores the immune basis of glomerular diseases and the mechanisms of podocyte injury. Pioneering work from this lab led to the identification of PLA2R (phospholipase A2 receptor) as the major target antigen in membranous nephropathy in 2009 and THSD7A (thrombospondin type-1 domain-containing 7A) as a minor target antigen in membranous nephropathy in 2014. These discoveries are considered one of the most ground-breaking discoveries in nephrology in the last 20 years. In addition to basic research, this lab is also engaged in cutting-edge translational research using tissue samples and data from participants enrolled in the Nephrotic Syndrome Study Network (NEPTUNE) to better characterize molecular and genetic mechanisms of membranous nephropathy.
Five selected publications:
1. Yuan H et al. Nephrin dissociates from actin and its expression is reduced in early experimental membranous nephropathy. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, 2002. PMID 11912254
2. Beck LH et al. M-type phospholipase A2 receptor as target antigen in idiopathic membranous nephropathy. New England Journal of Medicine, 2009. PMID: 25394321
3. Beck LH et al. Rituximab-induced depletion of anti-PLA2R autoantibodies predicts response in membranous nephropathy. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, 2012. PMID 21784898
4. Tomas NM and Beck LH et al. Thrombospondin type-1 domain-containing 7A in idiopathic membranous nephropathy. New England Journal of Medicine, 2014. PMID: 25394321
5. Larsen CP et al. LDL Receptor-Related Protein 2 (Megalin) as a Target Antigen in Human Kidney Anti-Brush Border Antibody Disease. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, 2018, PMID: 29074737