Research Week 2022 – Helen Lyo, MD
Title: The Performance of Fracture Risk Scores in Patients with IBD
Authors: Helen Lyo, Matt Custodio, Alan Moss
Background: ACG guidelines recommend risk-stratifying patients with IBD for risk of osteoporotic fractures. Fracture risk scores are preferred over universal bone density scans due to the low fracture prevalence overall. We sought to compare two scoring systems in one cohort to quantify their test characteristics in identifying low bone mineral density in patients with IBD.
Methods: We identified patients with IBD who had risk assessment and DEXA scans from a safety net health network. We collected demographic, FRAX score, QFracture score and DEXA results. The primary outcome of interest was an abnormal DEXA scan (T-score <-1).
Results: A cohort of 72 patients with baseline and follow-up data were included. Demographic data showed mean age of 52, 76% females, 55% Caucasians, 5% with tobacco use, 42% with alcohol use, 4% with previous fractures, and 61% with exposure to steroids for longer than 3 months. Mean t-score from DXA scans was -1.1. Only 5/78 had a history of prior bone fractures. Based on DEXA scores, 47% had osteopenia, and 10% had osteoporosis. Mean FRAX score was 8.5 with 8% of patients having high risk of fractures.
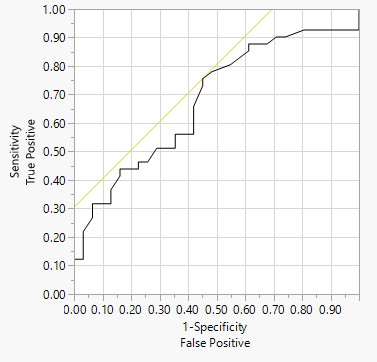
The FRAX score (without BMD) had an AUC of 0.68 to predict a DEXA T-score <-1. In contrast, the QFracture score had an AUC of 0.58 for this outcome.
Conclusions: In an ‘at-risk’ cohort of patient with IBD, the test characteristics of risk scores was modest to predict DEXA results. A prospective study of risk factors and BMD quantification in patients would be required to identify an IBD-specific risk score.
Image 1. ROC Curve of FRAX score and Abnormal DXA