Useful experimental models
Examples:
GFP-labeled DNA of Megakaryocytes in vivo:
An in vivo model with GFP-Histone labeled megakaryocytes.
Papadantonakis N, Makitalo M, McCrann DJ, Liu K, Nguyen HG, Martin G, Patel-Hett S, Italiano JE, Ravid K. Direct visualization of the endomitotic cell cycle in living megakaryocytes: differential patterns in low and high ploidy cells. Cell Cycle. 2008 Aug;7(15):2352-6. Epub 2008 May 21.
A Transgenic Mouse Model:
Conditional expression of genes in the megakaryocyte lineage in vivo.
Nguyen HG, Yu G, Makitalo M, Yang D, Xie HX, Jones MR, Ravid K. Conditional overexpression of transgenes in megakaryocytes and platelets in vivo.Blood. 2005 Sep 1;106(5):1559-64. Epub 2005 May 12.
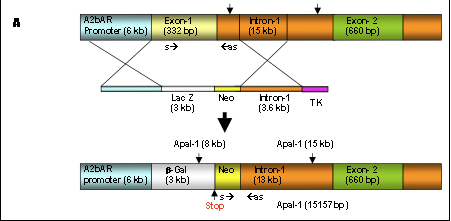
A Knock Out Mouse Model:
The first A2b adenosine receptor knock out mouse model, also with b-galactosidase knocked in instead of the deleted gene. This model has proven to be crucial for exploring the role of this receptor in inflammation, atherosclerosis and tissue regeneration.
Yang D, Zhang Y, Nguyen HG, Koupenova M, Chauhan AK, Makitalo M, Jones MR, St Hilaire C, Seldin DC, Toselli P, Lamperti E, Schreiber BM, Gavras H, Wagner DD, Ravid K. The A2B adenosine receptor protects against inflammation and excessive vascular adhesion.J Clin Invest. 2006 Jul;116(7):1913-23.