To view the Laboratory of Neurodegeneration’s PubMed publications, please click here.
Wolozin, B.L.: Towards an understanding of beta-lactamase catalysis. Undergraduate Thesis, 1980.
Wolozin, B.L., and Pasternak, G.W.: Classification of multiple morphine and enkephalin binding sites in the central nervous system. PNAS78(10):6181-6185, 1981.
Wolozin, B.L., Nishimura, S., and Pasternak, G.W.: The binding of Kappa and Sigma Opiates in rat brain. J. Neuroscience 2(6): 708-713, 1982.
Wolozin, B.L., Myerowitz, R., and Pratt, R.F.: Specific chemical modification of the readily nitrated tyrosine of the RTEM beta-lactamase and of bacillus cereus beta-lactamise I. The role of tyrosine in beta-lactamase catalysis. Biochem. Biophysics Acta 701(2):153-163, 1982.
Wolozin, B.L., Pruchnicki, A., Dickson, D.W., and Davies, P.: A neuronal antigen in the brains of Alzheimer patients. Science232:648-650, 1986.
Wolozin, B.L., and Davies, P.: Recent advances in the neurochemistry of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Clin. Psychiatry. 48:23-30, 1987.
Wolozin, B.L., and Davies, P.: Alzheimer related neuronal protein A68: specificity and distribution. Ann. Neurol. 22:521-526, 1987.
Davies, P., Scicutella, A., and Wolozin, B.L.: A new protein in Alzheimer’s Disease. Branberry Reports 27:459-471, 1987.
Wolozin, B.L.: A neuronal antigen in the brains of Alzheimer patients. Graduate Dissertation, 1987.
Wolozin, B.L., Scicutella, A., and Davies, P.: Re-expression of a developmentally regulated antigen in Down Syndrome and Alzheimer’s Disease. PNAS 85:6202-6206, 1988.
Hyman, B.T., Van Hoesen, G.W., Wolozin, B.L., Davies, P., and Damasio, A.R.: Alz-50 antibody recognizes Alzheimer-related neuronal changes. Ann. Neurol. 27:371-379, 1988.
Wolozin, B.L.: Immunochemical approaches to the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease. In: Becker, R.E., and Giacobini, E. (Eds.) Alzheimer’s Disease. Current Research in Early Diagnosis, Taylor and Francis, New York: 1990;
Lesch, K.P., Aulakh, C.S., Tolliver, T.J., Hill, J.L., Wolozin, B.L., and Murphy, D.L.: Differential effects of long-term lithium and carbamazepine administration on Gs_ and Gi_ protein in rat brain. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 207:355-359, 1991.
Wolozin, B.L., Sunderland, T., Zheng, B.B., Resau, J., Dufy, B., Barker, J., Swerdlow, R.D., and Coon, H.: Continuous culture of neuroblasts from adult human olfactory epithelium. J. Mol. Neuroscience 3:137-146, 1992.
Wolozin, B.L., Bacic, M., Merrill, M.J., Lesch, K.P., Chen, C., Lebovics, R.S., and Sunderland, T.: Differential expression of carboxyl terminal derivatives of amyloid precursor protein among cell lines. J. Neurosci. Res. 33:163-169, 1992
Wolozin, B.L., Chung, D., Zheng, B.B., Lesch, K.P., Lebovics, R.S., and Sunderland, T.: The β/A4 domain of APP: Antigenic differences between cell lines. J. Neurosci. Res. 33:189-197, 1992.
Lesch, K.P., Hough, C.J., Aulakh, C.S., Wolozin, B.L., Tolliver, T.J., Hill, J.L., Chuang,D.M., and Murphy, D.L.: Fluoxetine modulated G protein ss , qq and a12 subunit mRNA expressed in rat brain. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 227:233-237, 1992.
Lesch, K.P., Aulakh, C.S., Wolozin, B.L., Tolliver, T.J., Hill, J.L., and Murphy, D.L.: 3-(2-Carboxypiperazin-4-yl)Propyl-1-phosphonic acid decreases NMDA receptor mRNA. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 227:109-111, 1992.
Lesch, K.P., Aulakh, C.S., Wolozin, B.L., and Murphy, D.L.: Serotonin (5-HT) receptor, 5-HT transporter and protein-effector expression: Implications for depression. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 71:49-60, 1992.
Lesch, K.P., Aulakh, C.S., Wolozin, B.L., Tolliver, T.J., Hill, J.L., and Murphy, D.L.: Regional brain expression of serotonin transporter mRNA and its regulation by reuptake inhibiting antidepressants. Mol. Brain Res. 17:31-35, 1993.
Wolozin, B.L., Lesch, K.P., Lebovics, R.S., and Sunderland, T.: Olfactory neuroblasts from Alzheimer donors: Studies on APP processing and cell regulation. Biol. Psychiatry. 34:824-838, 1993.
Lesch, K.P., Wolozin, B.L., Estler, H.C., Murphy, D.L., and Riederer, P.: Isolation of a cDNA encoding the human brain serotonin transporter.J. Neural Transm. 91: 67-72, 1993.
Lesch, K.P., Aulakh, C.S., Wolozin, B.L., Riederer, P., Hill, J.L., and Murphy, D.L.: Norepinephrine, serotonin and vesicular monoamine transporter in depression and bipolar disorder: Expression during long-term antidepressant treatment. Neuropsychopharmacology9:34S-35S, 1993.
Wolozin, B.L.: The processing of amyloid precursor protein. Foundation Ipsen: Alzheimer Actualities 7:6-8, 1993.
Lesch, K.P., Gross, J., Wolozin, B.L., Murphy, D.L., and Riederer, P.: Extensive sequence divergence between the human and rat brain vesicular monoamine transporter: Possible molecular basis for species differences in the susceptibility to MPP+. J. Neural Transm. 93:75-82, 1993.
Lesch, K.P., Wolozin, B.L., Murphy, D.L., and Reiderer, P.: Primary structure of the human platelet serotonin uptake site: Identity with the brain serotonin transporter. J. Neurochem. 60:2319-2322, 1993.
Johnson, G., Brane, D., Basaric-Keys, J., Lebovics, R.S., Merril, C.R., Sunderland, T., and Wolozin, B.L.: Protein alterations inolfactory neuroblasts from Alzheimer donors. Neurobiol. Aging 15:675-680, 1994.
Lesch, K.-P., Balling, U., Gross, J., Strauss, K., Wolozin, B.L., Murphy, D.L., and Riederer, P.: Organization of the human serotonin transporter gene. J. Neural Transm. 95: 157-162, 1994.
Lesch, K.P., Gross, J., Wolozin, B.L., Franzek, E., Riederer, P., Murphy, D.L., Direct Sequencing of the reserpine-sensitive vesicular monoamine transporter complementary DNA in unipolar depression and manic-depressive illness. Psychiatric Genetics 4: 153-90 (1994).
Games, D., Adams, D., Alessandrini, R., Barbour, R., Berthelette, P., Blackwell, C., Carr, T., Clemens, J., Donaldson, T., Gillespie, F., Guido, T., Hagopian, S., Johnson‑Wood, K., Khan, K., Lee, M., Leibowitz, P., Lieberburg, I., Little, S., Masliah, E., McConlogue, L., Montoya-Zavala, M., Mucke, L., Paganini, L., Penniman, E., Power, M., Schenk, D., Seubert, P., Snyder, B., Soriano, F., Tan, Hua., Vitale, J., Wadsworth, S.,Wolozin, B., and Zhao, J.: Development of neuropathology similar to Alzheimer’s Disease in transgenic mice overexpressing the 717 V-F β-amyloid precursor protein. Nature, 373: 523-8, 1995.
Luo, Y Q. , Hirashima, N., Li, Y.H., Alkon, D.L., Sunderland, T., Etcheberrigaray, R., and Wolozin, B.L.: Physiological levels of b-amyloid increase tyrosine phosphorylation and cytosolic calcium. Brain Res., 681: 65-74 (1995).
Wolozin,B., Hirashima, N., Luo, Y.,Li, Y.H., Alkon, D.L., Etcheberrigaray, R. and Sunderland, T., Transforming growth factor induces a responsive calcium fluxes in neurons. NeuroReport, 6: 1301-5 (1995).
Lesch, K.P., Franzek, E., Gross, J., Wolozin, B.L., Riederer, P., and Murphy, D.L.: Primary Structure of the Serotonin transporter in unipolar and bipolar disorder. Biol. Psychiatry. 37: 215-23 (1995).
Iwasaki, K., Sunderland, T., Kusiak, J.W. and Wolozin, B., Changes in gene transcription during a_-mediated cell death. Mol. Psych. 1:65-71 (1996).
Wolozin, B., Luo, Y., and Wood, K.: Neuronal Loss and Aging in Cellular Aging and Cell Death, Eds. N.J. Holbrook, G.R. Martin and R. A. Lockshin (John Wiley & Sons, Inc., NY) 283-302.
Wolozin, B.L., Basaric-Keys, J., Canter, R., VanderPutten, D., and Sunderland, T.: Differential regulation of APP by apolipoprotein E3 and E4. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 777:322-6 (1996).
Wolozin, B., Basaric-Keys, J., Canter, R., Li, Y., Strickland, D and Sunderland, T., Differential regulation of APP secretion by apolipoprotein E3 and E4, Neurodegenerative Diseases ‘95: Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms. Ed. G. Fiskum (Plenum, Press, NY) 97-102.
Luo, Y., Sunderland, T. and Wolozin, B., Physiologic Levels of b-Amyloid Activate PI3-Kinase with the Involvement of Tyrosine Phosphorylation. J. Neurochem. 67:978-987 (1996).
Vawter, M.P., Basaric-Keys, J., Li, Y., Lebovics, R.S., Lesch, K.P., Kulaga, H., Freed, W.J., Sunderland, T., Wolozin, B., Human olfactory neuroepithelial cells: Tyrosine phosphorylation and process extension are increased by the combination of IL1_, IL6, NGF and βFGF. Exp. Neurol.. 142:179-194, 1996.
Vito, P., Wolozin, B, Ganji, K, Iwasaki, K., Lacana, E. and D’Adamio, L. Requirement of the familial Alzheimer’s Disease gene PS-2 for apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 271:31025-31028, 1996.
Wolozin, B., Iwasaki, K, Vito, P., Sunderland, T., Ganji, K., Lacana, E., Zhao, B., Kusiak, J., Wasco, W. and D’Adamio, L. Participation of Presenilin-2 in apoptosis: Enhanced basal activity conferred by Alzheimer mutation. Science. 274:1710-1713, 1996.
Wolozin, B. Redoubling our effort in redox chemistry. Mol. Psych.1:352-355, 1996.
Luo, Y., Sunderland, T., Roth, G.S. and Wolozin, B. Physiological levels of _-amyloid peptide promote PC12 cell proliferation. Neurosci. Lett. 217:125-128, 1996.
Wolozin, B. ICE and apoptosis. Mol. Psych. 2:184-187, 1997.
Goldstein, B.J., Wolozin, B.L., Schwob, J.E. FGF2 supresses neuronogenesis of a cell line derived from rat olfactory epithelium. J. Neurobiol. 33:411-8, 1997.
Luo, Y., Hawver, D. B., Iwasaki, K., Sunderland, T., Roth, G. S. andWolozin, B. Physiological levels of ß‑amyloid peptide stimulate protein kinase C in PC12 cells. Brain Res. 769:287-95, 1997.
Wallace., W, Akar, C., Lyons, W.E., Kole, W.E., Egan, J., Wolozin, B., Amyloid precursor protein requires the insulin signaling pathway for neurotrophic activity. Molecular Brain Research 52: 213-227, 1997.
Wolozin, B., Alexander, P., Palacino, J. Regulation of apoptosis by presenilins. Neurobiol. Aging. 19 (1S): S23-7, 1998.
Takashima, A., Murayama, M., Murayama, O., Kohno, T., Honda, T., Yasutake, K., Nihonmatsu, N., Mercken, M., Yamaguchi, H., Sugihara, S., Wolozin, B. Presenilin 1 Associates with Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3b, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., USA. 95:9637-41, 1998.
Murayama M; Tanaka S; Palacino J; Murayama O; Honda T; Sun X; Yasutake K; Nihonmatsu N; Wolozin B; Takashima A. Direct association of presenilin-1 with beta-catenin. FEBS Lett 14: 433:73-7, 1998.
Wolozin, B., Jones, C., Maheshwari, S., Dukoff, R., Nagula, S., Shulman, N.R. and Sunderland, T., Physiologic levels of ß-amyloid augment platelet aggregation: Reduced activity of familial angiopathy-assoicated mutants. Mol. Psych. 3: 500-507, 1998
Wolozin, B. and Palacino, J., Presenilins and their role in apoptosis. In eds. C. Haass, The Molecular Biology of Alzheimer’s Disease. Harwood Academic Publishers, Australia. 1998. pp. 247-76
Abrams, MT, Kaufmann, WE, Rousseau, F, Oostra, BA, Wolozin, B, Taylor, CV, Lishaa, N, Morel, ML, Hoogenveen, A, Reiss, AL. FMR1 gene expression in olfactory neuroblasts from two males with fragile X syndrome. Am. J. Med. Gen. 82: 25-30, 1999.
Wolozin, B. Genes in Alzheimer’s Disease, in “Genes, Behaviour and Health”, (Advisory Committee on Health Research of the World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland). pp. 123-144, 1999.
Ostrerova, N., Petrucelli, L., Farrer, M., Mehta, N., Palacino, J., Hardy, J. and Wolozin, B. _-Synuclein shares physical and functional homology with 14-3-3 proteins. J. Neurosci. 19: 5782-91, 1999.
Sunderland T; Wolozin B; Galasko, D., Levy, J., Dukoff, R., Bahro, M., Lasser, R., Motter, R., Lehtimaki, T., Seubert, P., Longitudinal stability of CSF tau levels in Alzheimer patients. Biol. Psych. 46:750-5, 1999.
Palacino, J., Berechid, B., C. Eckman, S. Younkin, Alexander, P., Nye, J.,Wolozin, B. Regulation of APP processing by Presenilin 1 and 2 in Presenilin 1 knockout cells. J. Biol. Chem. 275: 215-222, 2000.
Wolozin, B. and Behl, C., Mechanisms of neurodegenerative disorders. Part A: Protein Aggregates. Arch. Neurol. 57: 793-6, 2000
Wolozin, B. and Behl, C., Mechanisms of neurodegenerative disorders. Part B: Control of cell death. Arch. Neurol. 57: 797-800, 2000
Ostrerova-Golts, N., Petrucelli, L., Hardy, J., Lee, J.M., Farer, M.,Wolozin, B., The A53T α-Synuclein Mutation Increases Iron-Dependent Aggregation and Toxicity. J. Neurosci. 20: 6048-54, 2000.
Choi, P., Ostrerova-Golts, N., Sparkman, D., Cochran, E., Lee, J.M.,Wolozin, B., Parkin is Metabolized by the Ubiquitin/Proteosome System, NeuroReport 11: 2635 – 9, 2000.
*Wolozin, B.L., Kellman, W., Ruosseau, P., Celesia, G.G. and Siegel, G., Decreased Prevalence of Alzheimer’s Disease, Associated with HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors. Archives Neurol., 57: 1439 – 1443, 2000. *Reviewed in the Editors Choice column of Science, 290: 1857 (2000), and discussed in Science, 294: 506-7 (2001).
Wolozin, B., A fluid connection: Cholesterol and Ab, (Invited Commentary) PNAS 98:5371-3 (2001).
Wolozin, B., Peering into proteolylsis with presenilins, (Invited Commentary) Journal Alz. Dis. 3: 191-3 (2001).
Wolozin, B., Golts, N., Choi, P., Frasier, M., Snyder, H. and Palacino, J., Looking beyond b-amyloid: a-Synuclein and Neurodegeneration. Research and Practice in Alzheimer’s disease, Vol. 4, 2001.
Choi, P., Golts, N., Snyder, H., Petrucelli, L., Chong, M., Hardy, J.,Sparkman, D., Cochran, E., Lee, J.M., Wolozin, B., Co-association of parkin and α-synuclein, NeuroReport. 12: 2839-45 (2001).
Palacino, J.J., Murphy, M.P., Murayama, O., Iwasaki, K., Fujiwara, M., Takashima, A., Golde, T.E., Wolozin, B., Presenilin 1 Regulates β-Catenin-Mediated Transcription in a GSK 3b-Independent Fashion JBC 276(42):38563-38569 (2001).
Ahn, B. H., Rhim, H., Kim, S. Y., Sung, Y. M., Lee, M. Y., Choi, J. Y.,Wolozin, B., Chang, J. S., Lee, Y. H., Kwon, T. K., Chung, K. C., Yoon, S. H., Hahn, S. J., Kim, M. S., Jo, Y. H., and Min, D. S. Alpha-synuclein interacts with phospholipase D isozymes and inhibits pervanadate induced phospholipase D activation in human embryonic kidney 293 cells. J Biol Chem. 277(14):12334-42 (2002).
Wolozin, B. and Siegel, G., Response to letter: Statins and Dementia. Archives Neurol. 58: 1169 (2001).
Wolozin, B. and Siegel, G., Response to Letter: Statin-Alzheimer Disease Association Not Yet Proven. Archives Neurol. 58: 1022 (2001).
Wolozin, B. and Siegel, G., Response to Letter: Statin Therapy and the Prevention of Dementia. Archives Neurol. 58: 1023 (2001)
Wolozin, B. and Golts, N., Synuclein, iron and Parkinson’s disease, The Neuroscientist. 8(1): 22-32 (2002).
Golts, N., Snyder, H., Frasier, M., Theisler, C., Choi, P., Wolozin, B. Magnesium inhibits spontaneous and iron-induced aggregation of alpha –synuclein. J. Biol. Chem. 277:16116-23 (2002).
Wolozin, B., Cholesterol and Alzheimer’s disease. Biochemical Society Transactions 30(4): 525-30 (2002).
Petrucelli, L., O’Farrell, C., Kehoe, K., Vink, L., Lockhart, P.J., Baptista, M., Wolozin, B. Choi, P., Farrer, M., Hardy, J., Cookson, M.R., Parkin protects against the toxicity associated with over-expression of synuclein: Proteasome dysfunction selectively affects dopaminergic neurons. Neuron 36:1007-19 (2002).
Egashira N, Iwasaki K, Ishibashi M, Hatip-Al-Khatib I, Wolozin B, Mishima K, Irie K and Fujiwara M., Hypoxia Enhances beta-Amyloid-Induced Apoptosis in Rat Cultured Hippocampal Neurons. Japanese J Pharmacol 90:321-327 (2002).
Wolozin, B., Cyp46 (24-Cholesterol Hydroxylase): A genetic risk factor for Alzheimer’s Disease. Archives of Neurology 60:16-8 (2003) (invited commentary).
Snyder, H., Mensah, K., Theisler, C., Lee, J. M., Matouschek, A. andWolozin, B., Aggregated and Monomeric a-Synuclein bind to the S6’ Proteasomal Protein and Inhibit Proteasomal Function. J. Biol. Chem. 278:11753-9 2003.
Choi P., Snyder, H.,Petrucelli L., Theisler, C., Chong M., Zhang Y., Lim K., Chung K., Kehoe K., L. D’Adamio, Lee J.M., Cochran E., Bowser R., Dawson T., Wolozin, B., SEPT5 v2 is a parkin-binding protein. Mol. Brain Res. 117:179-189 (2003).
Perry G, Castellani RJ, Smith MA, Harris PL, Kubat Z, Ghanbari K, Jones PK, Cordone G, Tabaton M, Wolozin B, Ghanbari H., Oxidative damage in the olfactory system in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol (Berl). 106:552-6 (2003).
Pappolla MA, Bryant-Thomas TK, Herbert D, Pacheco J, Fabra Garcia M, Manjon M, Girones X, Henry TL, Matsubara E, Zambon D, Wolozin B, Sano M, Cruz-Sanchez FF, Thal LJ, Petanceska SS, Refolo LM. Mild hypercholesterolemia is an early risk factor for the development of Alzheimer amyloid pathology. Neurology.61:199-205 (2003).
Wolozin, B. Cholesterol and the Biology of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron 41:7010 (2004) (Invited Commentary).
Petrucelli, L., Dickson, D., Kehoe, K., Taylor, J., Snyder, H., Grover, A., McGowan, E., Lewis, J., Dillman, W., Browne, S.E., Voellmey, R., Tsuboi, Y., Dawson., T.M., Wolozin, B., Hardy, J., Hutton, M., CHIP and Hsp70 regulate tau ubiquitination, degradation and aggregation. Human Molecular Genetics 13:703-14 (2004).
Frasier, M., Wolozin, B., Following the leader: Fibrillization of a-synuclein and tau. Exp. Neurol. 187:235-9 (2004) (Invited Commentary).
Wolozin, B., Apo E Receptor LR11: Intersections between Neurodegeneration and Cholesterol Metabolism. Arch. Neurol. 61:1178-80 (2004) (Invited commentary).
Wolozin, B., Brown, J., Theisler, C., Silberman, S., The Cellular Biochemistry of Cholesterol and Statins: Insights into the Pathophysiology and Therapy of Alzheimer’s Disease. CNS Drug Reviews 10:127-46 (2004).
Ghanbari HA, Ghanbari K, Harris PL, Jones PK, Kubat Z, Castellani RJ, Wolozin BL, Smith MA, Perry G., Oxidative damage in cultured human olfactory neurons from Alzheimer’s disease patients. Aging Cell. 3:41-4 (2004).
Brown, J., Theisler, C., Silberman, S., Magnuson, D., Russell, D.W., Marquez-Sterling, N., Lee, J.M., Yager, D., Crowley, J., Sambamurti, K., Rahman, M., Reiss, A.B., Eckman, C.B., Wolozin, B., Differential Expression of Cholesterol Hydroxylases in Alzheimer’s disease. JBC 279:34674-81 (2004).
Frasier, M., Walzer, M., McCarthy, L., Magnuson, D., Lee, J.M., Haas, C., Kahle, P. and Wolozin, B., Tau phosphorylation increases in symptomatic mice over-expressing A30P α-synuclein. Exp. Neurol, 192:274-87 (2005).
Poon, H.F., Frasier, M., Kahle, P., Haass, C., Sherve, N., Calabrese, V., Wolozin, B., Butterfield, D.A. Mitochondrial associated Metabolic Proteins are Selectively Oxidized in A30P a-Synuclein Transgenic Mice – A Model of Familial Parkinson’s Disease. Neurobio. Dis., 18:492-8 (2005).
Snyder, H., Mensah, K., Hashimoto, M., Surgucheva, I.G., Festoff, B., Surguchov, A., Masliah, E., Matouschek, A., Wolozin, B. β-Synuclein Reduces Proteasomal Inhibition by a-Synuclein but not g-Synuclein. JBC 280:7562-9 (2005).
Snyder, H., Wolozin, B., Pathological proteins in Parkinson’s disease: focus on the proteasome. J Mol Neurosci. 24:425-42 (2005).
Lee, TA Wolozin*, B, Weiss, K, Bednar, MM, Assessment of the Emergence of Alzheimer’s Disease Following Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery or Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty. J. Alzheimer’s Disease 7:319-24 (2005) (*Corresponding Author).
Ved, R., Saha, S., Sluder, A., Westlund, B., Burnam, L., Hoener, M., Przedborsky, S., Alfonso, A., Liu, L., Wolozin, B. Similar Patterns of Mitochondrial Vulnerability and Rescue Induced by Genetic Modification of a-Synuclein, Parkin and DJ-1 in C. Elegans. JBC, 280(52):42655-68 (2005).
Wolozin, B., J. Manger, R. Bryant, J. Cordy, R.C.Green and A. McKee. Cholesterol, Alzheimer’s disease and Statins: Re-assessing the relationship between cholesterol, statins and Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathologica Suppl. 185:63-70 (2006).
Frasier, M., Frausto, S., Lewicki, D., Golbe, L., Wolozin, B., DJ-1 Expression Increases in Mice Over-Expressing A30P a-Synuclein. In ALZHEIMER’S AND PARKINSON’S DISEASES: INSIGHTS,PROGRESS AND PERSPECTIVES (Eds., Hanin and Fisher, Springer, NY) (2008).
Wolozin, H and Wolozin, B., The Unconscious in Economic Decision-Making: Convergent Voices. Journal of Socio-Economics (in press, 2006).
Wolozin, B., Interpreting Clinical Studies of Putative Therapeutics for Alzheimer’s disease. In, ed. Cuello, C., Pharmacological and Mechanisms in Alzheimer’s Therapeutics (Springer, NY, 2006).
Wolozin, B. and Bednar, M. M., Interventions for Heart Disease and Their Effects on Alzheimer’s disease, In, ed., de la Torre, J. C., Impact of Heart Disease and Stroke on Alzheimer’s Disease, Neurologic Research 28:630 – 6 (2006).
Wolozin, B., Cholesterol, Statins and Alzheimer’s disease: Past, Present and Future, In, ed. Sun, M. K., Research Progress in Alzheimer’s Disease and Dementia (2006).
Takashima A, Shimojo M, Wolozin B. The players on the gamma-secretase team. Nat Med. Jul;12(7):766-767 (2006).
Bednar M.M., Lee TA, Wolozin B, Weiss K.B.. Coronary artery bypass grafting is not a risk factor for dementia or Alzheimer disease. Neurology. Jun 13;66(11):1785 (2006).
Cordy, J.M. and Wolozin, B, Cholesterol and Alzheimer’s disease. In eds Barrow C.J., Small D.H.. Abeta Peptide and Alzheimer’s Disease: Celebrating a Century of Research. (London: Springer-Verlag, 2006, 312 pp).
Wolozin, B., Wang, SW, Lee, A, Lee TA, Kazis, LE, Use of simvastatin is associated with a reduction in the incidence of dementia and Parkinson’s disease. BMC Medicine 5:20 (2007). PMID: 17640385
Wolozin, B., Saha, S., Guillily, M., Ferree, A., Riley, M., Investigating Convergent Actions of Genes Linked to Familial Parkinson’s Disease. Neurodegenerative Diseases, 5:182-5 (2008). PMID: 18322385
Zerbinatti, CV, Cordy, JM, Chen, CD, Guillily, M, Suon, S, Ray, WJ, Seabrook, GR, Abraham, CR, Wolozin, B, Oxysterol-binding protein-1 (OSBP1) modulates processing and trafficking of the amyloid precursor protein. Mol. Neurodegen 3:5 (2008). PMID: 18348724
Tezapsidis N, Johnston JM, Smith MA, Ashford JW, Casadesus G, Robakis NK, Wolozin B, Perry G, Zhu X, Greco SJ, Sarkar S., Leptin: a novel therapeutic strategy for Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alz. Dis. 29:731-40 (2009). PMID: 19387109
Solomon A., Kåreholt I, Ngandu T, Wolozin B, Macdonald SW, Winblad B, Nissinen A, Tuomilehto J, Soininen H, Kivipelto M. Serum total cholesterol, statins and cognition in non-demented elderly. Neurobiol Aging. 30: 1006-9 (2009).
Saha, S., Guililly, M., Ferree, A., Lanceta, J., Chan, D., Ghosh, J., Segal, L., Raghavan, K., Hsu, C., Cordy, J., Kuwahara, T., Iwatsubo, T., Goldstein, L., Cookson, MR, and Wolozin, B., LRRK2 modulates vulnerability to mitochondrial dysfunction in C. elegans J. Neurosci, 29:9210-8 (2009). PMID: 19625511
Solomon A, Kivipelto M, Wolozin B, Zhou J, Whitmer RA., Midlife Serum Cholesterol and Increased Risk of Alzheimer’s and Vascular Dementia Three Decades Later. Dementia Geriatric Cogn. Disord. 28:75-80 (2009). PMID: 19648749
Hsu, CH, Chan, D, Greggio, E., Saha, S., Guillily, M.D., Ferree, A., Raghavan, K., Shen, GC, Segal, L., Ryu, H., Cookson, M. R., Wolozin, B., MKK6 binds and regulates expression of Parkinson’s disease-related protein LRRK2. J. Neurochem. 112(6): 1593-604 (2010). PMID: 20067578
Hsu, CH, Chan, D. and Wolozin, B., LRRK2 and the stress response: Interaction with MKK and JNK interacting proteins, Neurodegen. Dis. 7(1-3):68-75 (2010). PMID: 20173330
*Li, N.C., Lee, A., Whitmer, R. A., Kivipelto, M., Lawler, E., Kazis, L.E. and Wolozin, B., Use of Angiotensin Receptor Blockers and the Risk of Dementia in a Predominantly Male Population: A Prospective Cohort Analysis. BMJ 340:b5465 doi: 10.1136/bmj.b5465 (2010). PMID: 20068258 * Commentary on the manuscript in the same issue of BMJ.
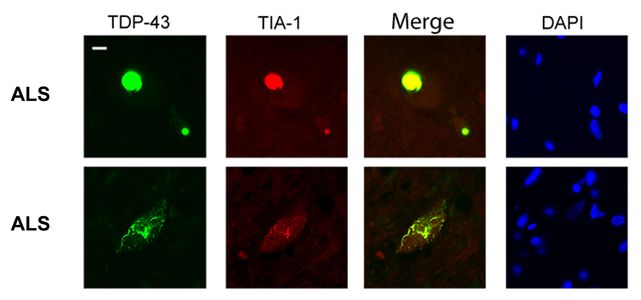
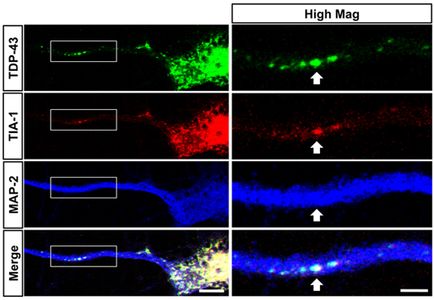
Liu-Yesucevitz, L., Bilgutay, A., Zhang, Y-Z., Mehta, T., Citro, A., Zaruur, N., McKee, A., Bowser, R., Sherman, M., Petrucelli, L. andWolozin, B., Tar DNA Binding Protein-43 (TDP-43) Associates with Stress Granules: Analysis of Cultured Cells and Pathological Brain Tissue. Plos ONE (5(10). pii: e13250), (2010) PMID: 20948999.
Kumar, A., Greggio, E., Beilina, A., Kaganovich, A., Chan, D., Taymans, J.M., Wolozin, B., Cookson, M.R., The Parkinson’s disease associated LRRK2 exhibits weaker in vitro phosphorylation of 4E-BP compared to autophosphorylation. Plos ONE 15(1):E8730 (2010). PMID: 20090955
Carballo-Carbajal, I., Weber-Endress, S.U.K., Klein, C., Patenge, N., Rovelli, G., Wolozin, B., Gasser, T. and Kahle P.J., Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 induces a-synuclein expression via the extracellular signal regulated kinase pathway. Cell Signaling 22(5):821-7 (2010). PMID: 20074637
Solomon A,Sippola R,Soininen H,Wolozin B,Tuomilehto J,Laatikainen T, Kivipelto M., Lipid-lowering treatment is related to decreased risk of dementia: a population-based study (FINRISK), 7(1-3):180-2 (2010). PMID: 20224281
Vanderweyde T, Bednar MM, Forman SA and Wolozin B, Iatrogenic risk factors for Alzheimer’s disease: Surgery and Anesthesia. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease. (2010) Epub. PMID: 20858967
Wolozin, B. , Lee, A., Li, N.C., Kazis, L.E., Pharmaco-epidemiological Studies Using the Veterans Affairs Health System Decision Support System Database, in Efficient Decision Support Systems: Practice and Challenges – From Current to Future / Book 3 (2011)(ISBN 978-953-308-63-9). Intechweb.org
Devine MJ, Kaganovich A, Ryten M, Mamais A, Trabzuni D, Manzoni C, McGoldrick P, Chan D, Dillman A, Zerle J, Horan S, Taanman JW, Hardy J, Marti-Masso JF, Healey D, Schapira AH, Wolozin B, Bandopadhyay R, Cookson MR, van der Brug MP, Lewis PA., Pathogenic LRRK2 Mutations Do Not Alter Gene Expression in Cell Model Systems or Human Brain Tissue. PLoS One. 2011;6(7):e22489. Epub 2011 Jul 22. PMID: 21799870.
Chan, D., Citro, A., Cordy, J.M., Shen, G.C., Wolozin, B., Rac1 Rescues Neurite Retraction Caused By G2019s Leucine-Rich Repeat Kinase 2 (Lrrk2), J. Biol. Chem. 286(18):16140-9 (2011). PMID: 21454543.
Wolozin B, Gabel C, Ferree A, Guillily M, Ebata A., Watching worms whither: modeling neurodegeneration in C. elegans, Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2011;100:499-514, PMID: 21377635.
Liu-Yesucevitz, L. Bassell, G.J., Gitler, A.D., Hart, A.C., Klann, E., Richter, J.D., Warren, S.T. and Wolozin, B., Local RNA Translation at the Synapse and in Disease. J. Neurosci. (in press).
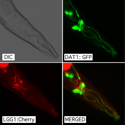
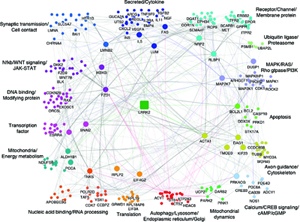
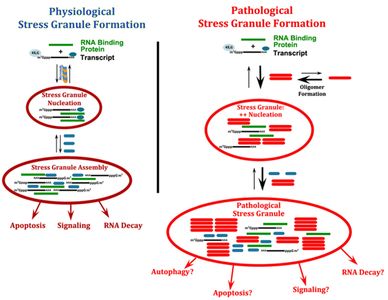
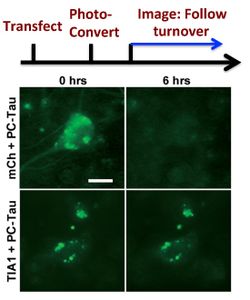
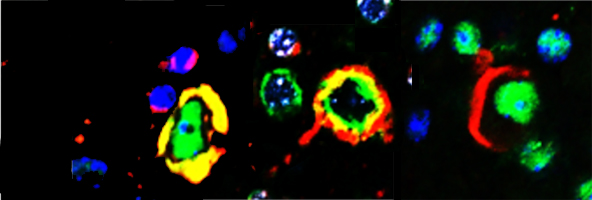 Dr. Wolozin was recently given the Zenith Award to propel his studies of the roles of RNA binding proteins in Alzheimer’s disease. We recently discovered that the Alzheimer brain is characterized by massive accumulation of RNA binding proteins causing pathological stress granules. Using immunoprecipitation combined with mass spectrometry, we showed that tau contributes to the regulation of RNA metabolism. Tau regulates the proteins that interact with RNA binding proteins, such as TIA1. Phosphorylation and somatodendritic localization of tau (which are pathological hallmarks of disease) contribute to the translational stress response by promoting stress granule formation. The converse is also true: tau localizes to stress granules. Persistent stress granules increase tau stability and promote tau aggregation. This work suggests that stress granules can serve as a nidus for tau pathology.
Dr. Wolozin was recently given the Zenith Award to propel his studies of the roles of RNA binding proteins in Alzheimer’s disease. We recently discovered that the Alzheimer brain is characterized by massive accumulation of RNA binding proteins causing pathological stress granules. Using immunoprecipitation combined with mass spectrometry, we showed that tau contributes to the regulation of RNA metabolism. Tau regulates the proteins that interact with RNA binding proteins, such as TIA1. Phosphorylation and somatodendritic localization of tau (which are pathological hallmarks of disease) contribute to the translational stress response by promoting stress granule formation. The converse is also true: tau localizes to stress granules. Persistent stress granules increase tau stability and promote tau aggregation. This work suggests that stress granules can serve as a nidus for tau pathology.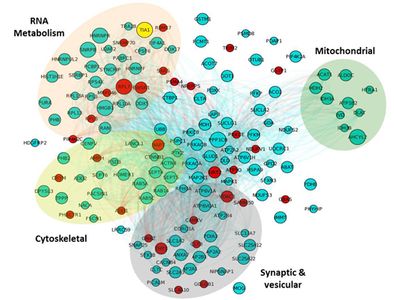



 Daniel Apicco, Graduate Student
Daniel Apicco, Graduate Student Brandon Maziuk, Graduate Student
Brandon Maziuk, Graduate Student Ali Al Abdullatif
Ali Al Abdullatif Bria Adams, Undergraduate
Bria Adams, Undergraduate Brandon Bedell, Undergraduate
Brandon Bedell, Undergraduate Emily Botelho, Undergraduate
Emily Botelho, Undergraduate Amanda Jeh, Undergraduate
Amanda Jeh, Undergraduate LiQun Liu, PhD
LiQun Liu, PhD Katie Youmans-Kidder, PhD Former Postdoctoral Fellow
Katie Youmans-Kidder, PhD Former Postdoctoral Fellow Joon Ying Boon, PhD Former Graduate Student
Joon Ying Boon, PhD Former Graduate Student Atsushi Ebata, PhD Former Graduate Student
Atsushi Ebata, PhD Former Graduate Student Chelsea Trengrove, PhD Former Graduate Student
Chelsea Trengrove, PhD Former Graduate Student Tara Vanderweyde, PhD Former Graduate Student
Tara Vanderweyde, PhD Former Graduate Student Isaac Goldszer Former Masters Student
Isaac Goldszer Former Masters Student Vivek Gowda Former Masters Student
Vivek Gowda Former Masters Student Shamol Saha, PhD Former Senior Research Scientist
Shamol Saha, PhD Former Senior Research Scientist Allison Citro Former Lab Staff
Allison Citro Former Lab Staff Alexander Hentschel Former Undergraduate Student
Alexander Hentschel Former Undergraduate Student Maria Iuliano Former Undergraduate Student
Maria Iuliano Former Undergraduate Student